Table of Contents
Treating and Coping with Sleep Apnea
 Obstructive sleep apnea, also called sleep apnea, can lead to fragmented sleep and low blood oxygen levels. For patient suffering from with sleep apnea, the combination of disturbed sleep and oxygen starvation may cause hypertension, heart disease and mood and memory problems. It is essential to learn ways to treat sleep apnea and how to cope with this sleep-related breathing disorder.
Obstructive sleep apnea, also called sleep apnea, can lead to fragmented sleep and low blood oxygen levels. For patient suffering from with sleep apnea, the combination of disturbed sleep and oxygen starvation may cause hypertension, heart disease and mood and memory problems. It is essential to learn ways to treat sleep apnea and how to cope with this sleep-related breathing disorder.
Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder where breathing is intermittent and frequently interrupted during sleep. The “apnea” in sleep apnea is a breathing pause that lasts at least ten seconds. Obstructive sleep apnea arises when the muscles in the back of the throat are unable to keep the airway open, despite efforts to breathe. Another form of sleep apnea is central sleep apnea where the brain fails to appropriately control breathing during sleep. Obstructive sleep apnea is far more common as compared to central sleep apnea.
Who can suffer from Sleep Apnea?
More than 18 million adults in America have sleep apnea, with over 30 million having sleep apnea symptoms. It is currently very challenging to estimate the prevalence of childhood OSA because of generally varying monitoring techniques. However, a minimum prevalence is likely to be between 2 to 3% for children without any other health conditions and prevalence as high as 10 to 20% in habitually snoring children. OSA occurs in all age groups and both sexes.
What Causes Sleep Apnea?
There are several factors that intensify sleep apnea risk including having a small upper airway, being overweight, having a recessed chin, small jaw or a large overbite, a large neck size, smoking and alcohol use, being age 40 or older, and ethnicity. Likewise, OSA seems to run in some families, suggesting a possible genetic source.
Sleep Apnea Symptoms
 Chronic snoring is a strong pointer of sleep apnea and should be assessed by a health professional. Since people with sleep apnea tend to be sleep deprived, they may suffer from sleeplessness and a variety of other symptoms such as difficulty concentrating, depression, sexual dysfunction, learning and memory difficulties, irritability, and falling asleep while at work, on the phone, or driving.
Chronic snoring is a strong pointer of sleep apnea and should be assessed by a health professional. Since people with sleep apnea tend to be sleep deprived, they may suffer from sleeplessness and a variety of other symptoms such as difficulty concentrating, depression, sexual dysfunction, learning and memory difficulties, irritability, and falling asleep while at work, on the phone, or driving.
However, a sleep expert may have the experience to treat sleep apnea without cpap. It is worthwhile to note that symptoms of sleep apnea can lead to health complications if left untreated. That includes congestive heart failure, cardiac arrhythmia, high blood pressure, heart attack, and stroke or depression.
Sleep Apnea Treatment
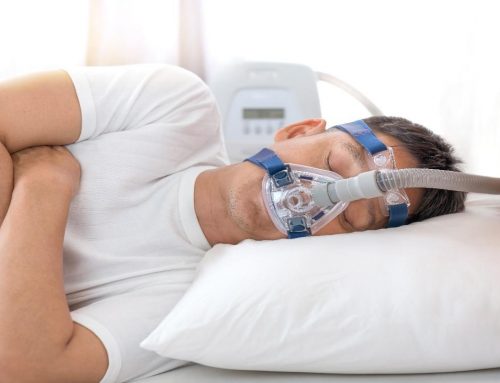
If you suspect you may have sleep apnea disorder, the ideal thing to do is consult your doctor to treat sleep apnea. The treatment of selection for obstructive sleep apnea is CPAP device. CPAP is a mask that fits over the nose or mouth, and softly blows air into the airway to assist in keeping it open during sleep. This method of treatment is highly effective. Using the sleep apnea machine as recommended by your doctor is very important.


 Shop
Shop